This is an old revision of the document!
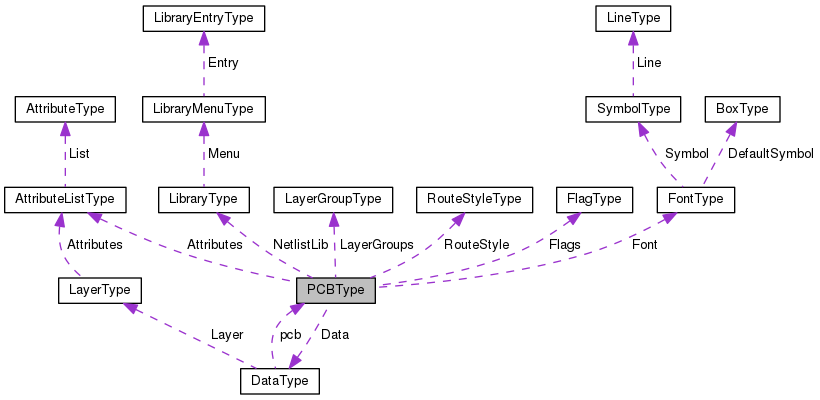
PCBType
PCBType is the main data structure
PCBType contain all the general information used in the program and it contains a pointer to the DataType
DataType
The DataType contains the actual data that defines our printed circuit board.
DataType is what's stored in the Buffers when you do cut/paste.
| Data Fields | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cardinal | ViaN | |
| Cardinal | ElementN | |
| Cardinal | RatN | |
| int | LayerN | |
| GList * | Via | Layer independent via's |
| GList * | Element | Layer independent elements |
| GList * | Rat | Layer independent rat-lines |
| rtree_t * | via_tree | |
| rtree_t * | element_tree | |
| rtree_t * | pin_tree | |
| rtree_t * | pad_tree | |
| rtree_t * | name_tree [3] | |
| rtree_t * | rat_tree | |
| struct PCBType * | pcb | A pointer back to the main data structure |
| LayerType | Layer [MAX_LAYER+2] | All layer dependent items |
| int | polyClip | |
The actual data is stored in the GList data elements. The rest is there for administrative purposes, to keep track of it all. Here I like to specially mention the rtree_t* data members. Although they have an administrative character the R-TREE data structure is heavily used in the PCB program.
GList
struct GList { gpointer data; GList *next; GList *prev; };
The GList struct is used for each element in a doubly-linked list.
Members:
| gpointer data | holds the element's data , which can be a pointer to any kind of data. |
| GList *next | contains the link to the next element in the list |
| GList *prev; | contains the link to the previous element in the list |
gpointer ⇒
typedef void* gpointer;
An untyped pointer. gpointer looks better and is easier to use than void*.
R-TREE
From Wikipedia: The key idea of the r-tree data structure is to group nearby objects and represent them with their minimum bounding rectangle in the next higher level of the tree; the “R” in R-tree is for rectangle. Since all objects lie within this bounding rectangle, a query that does not intersect the bounding rectangle also cannot intersect any of the contained objects. At the leaf level, each rectangle describes a single object; at higher levels the aggregation of an increasing number of objects. This can also be seen as an increasingly coarse approximation of the data set.
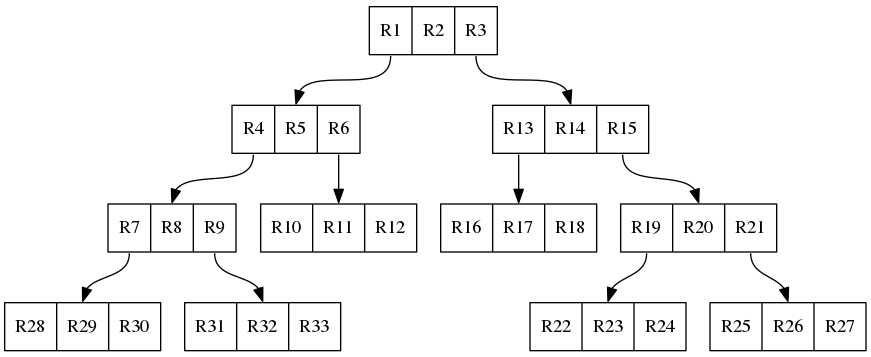
A general r-tree will look like this:
The bottom row of records are called leafs.
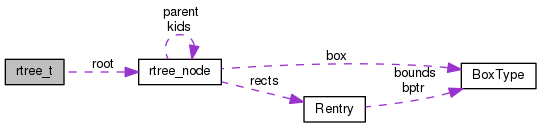
The rtree data structure PCB uses is:
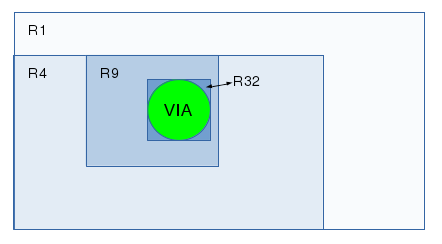
The r-tree data structure hold a copy of the where's what data. Meaning that it holds a list of every item on our canvas arranged in successively smaller boxes.